Qualification Requirements for Working and Teaching in the Middle East
K-12 International Schools:
- 4 year general BA university degree with PGCE or HDE Diploma
- B.Education Degree in Field of Specialization
- Generally 2 years post-graduate experience required
University ESL/Vocational Lecturers
- 4 year general BA university degree with TEFL/TESOL/DELTA
- Masters degrees preferred
- Generally 3 years post-graduate experience required
Other Professions
- 4 year general BA university degree in field of specialization
- Trade qualifications as per international standards
Salary and Benefits packages
- Competitive Tax free salary commensurate with the industry, qualifications/years of experience
- Paid annual flights from and to home country.
- Furnished accommodation | accommodation allowance.
- Transport to and from school or allowance.
- Medical Aid as per the UAE labour law.
- Legal work visa valid for 1 or 2 years
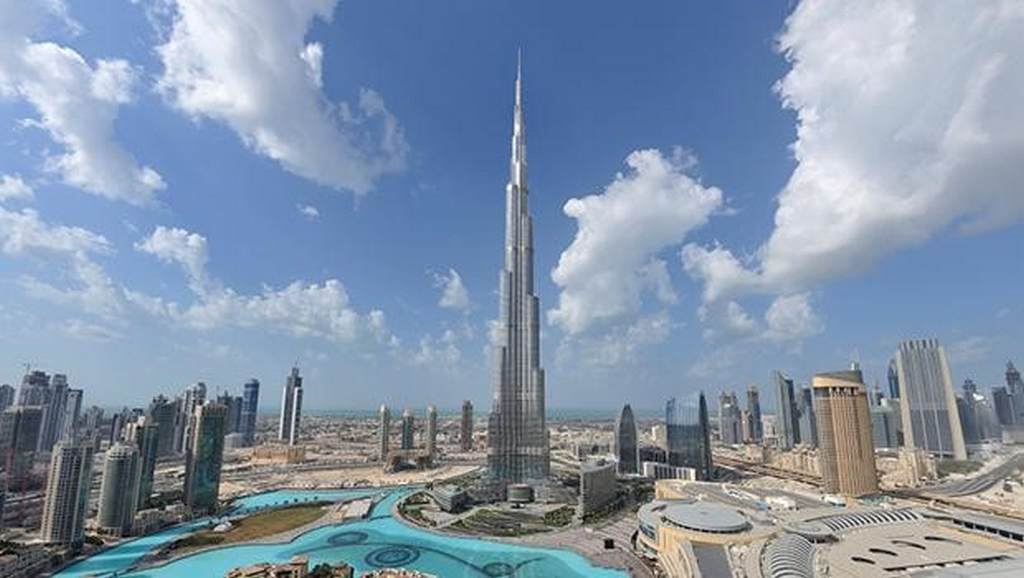
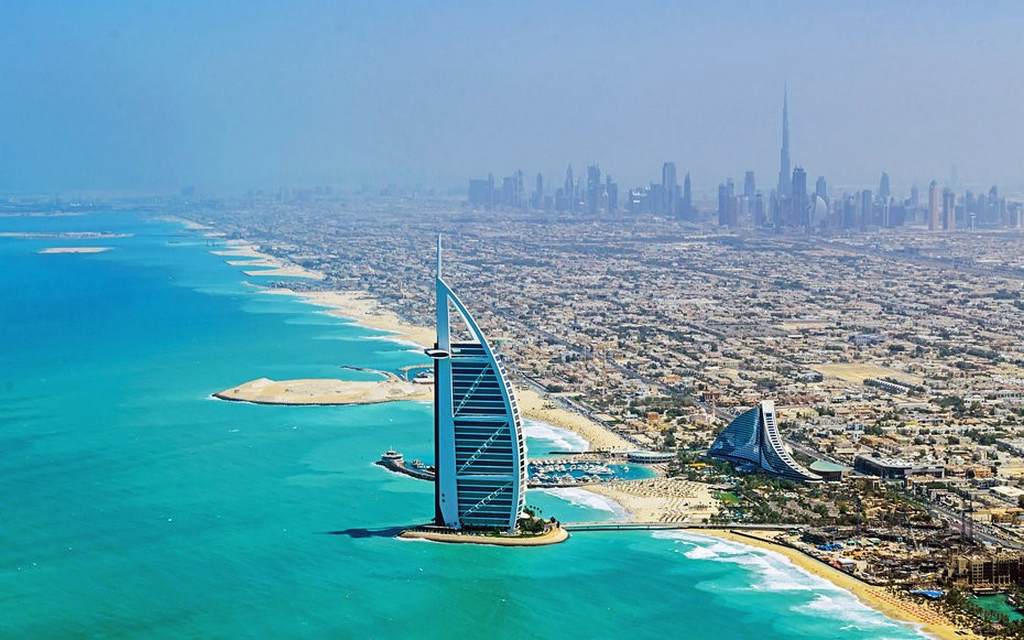
Working and teaching in the United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates, sometimes called the Emirates is a federal absolute monarchy at the southeast end of the Arabian Peninsula. In 2013, the UAE’s population was 9.2 million of which 1.4 million are Emirati citizens and 7.8 million expatriate workers.
The country is a federation of seven emirates, and was established on 2 December 1971. The constituent emirates are Abu Dhabi (which serves as the capital), Ajman, Dubai, Fujairah, Ras al-Khaimah, Sharjah and Umm al-Quwain.
Each emirate is governed by an absolute monarch; together, they jointly form the Federal Supreme Council. One of the monarchs (traditionally always the Emir of Abu Dhabi) is selected as the President of the United Arab Emirates. Islam is the official religion of the UAE.
The UAE’s oil reserves are the seventh-largest in the world while its natural gas reserves are the world’s seventeenth-largest. Sheikh Zayed, ruler of Abu Dhabi and the first President of the UAE, oversaw the development of the Emirates and steered oil revenues into healthcare, education and infrastructure. The UAE’s economy is the most diversified in the Gulf Cooperation Council, while its most populous city of Dubai is an important global city and an international aviation hub.
Quick Facts:
President: Khalifa bin Zayed Al Nahyan
Capital City: Abu Dhabi
International dialling code: +971
Currency: United Arab Emirates dirham (AED or Dhs)
Population: 9.206 million (2013)
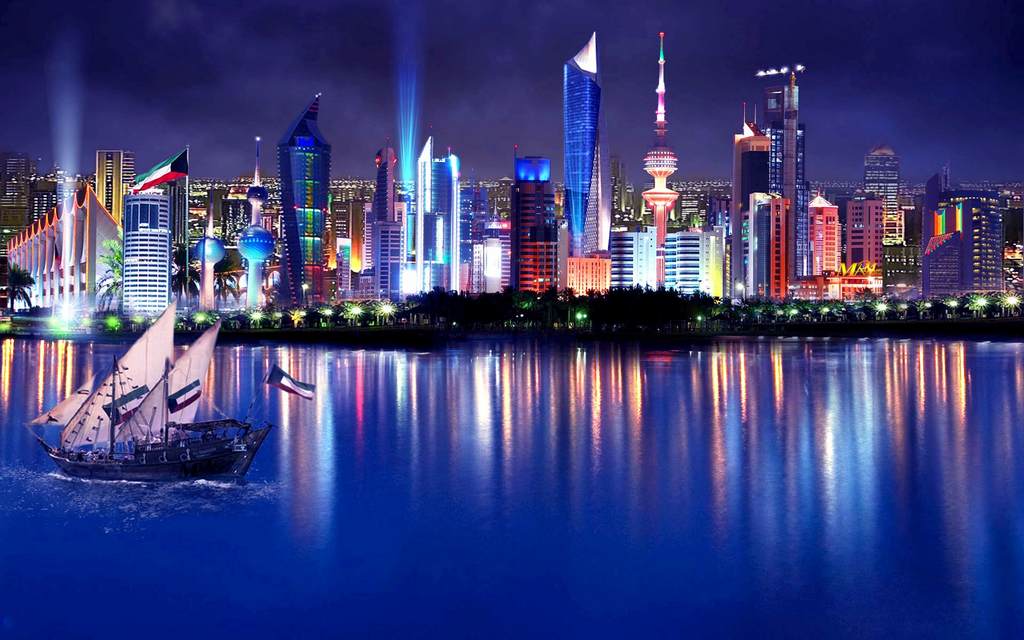
Working and Teaching in Kuwait
Kuwait, officially the State of Kuwait is a country in Western Asia. Situated in the northern edge of Eastern Arabia at the tip of the Persian Gulf, it shares borders with Iraq and Saudi Arabia. As of 2016, Kuwait has a population of 4.2 million people; 1.3 million are Kuwaitis and 2.9 million are expatriates. Expatriates account for 70% of the population.
Oil reserves were discovered in commercial quantities in 1938. From 1946 to 1982, the country underwent large-scale modernization. Islam is the official religion of Kuwait. It is a constitutional state with a semi-democratic political system. It has a high income economy backed by the world’s sixth largest oil reserves.
The Kuwaiti dinar is the highest valued currency in the world. According to the World Bank, the country has the fourth highest per capita income in the world.
The Constitution was promulgated in 1962. Kuwait is home to the largest opera house in the Middle East. The Kuwait National Cultural District is a member of the Global Cultural Districts Network. Kuwait is widely considered the “Hollywood of the Gulf” due to the popularity of its soap operas and theatre.
Quick Facts:
Capital City: Kuwait City
International dialing code: +965
Currency: Kuwaiti dinar (KD)
Population: 4.425 million (2016)
Government: Hereditary monarchy, Unitary state, Constitutional monarchy
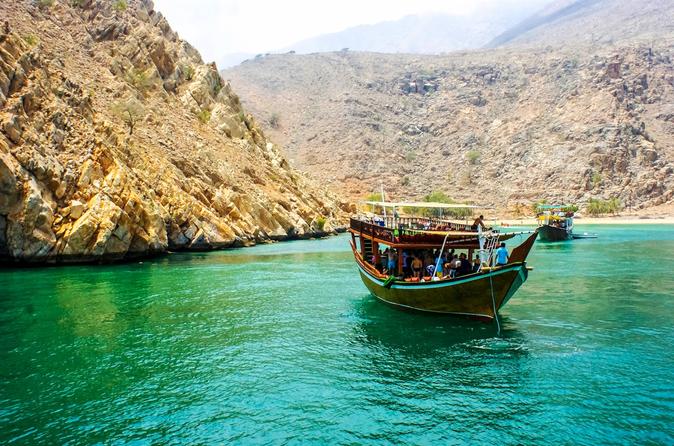
Working and Teaching in Oman
Oman,officially the Sultanate of Oman is an Arab country on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in Western Asia. It is the oldest independent state in the Arab world. Holding a strategically important position at the mouth of the Persian Gulf, the country shares land borders with the United Arab Emirates to the northwest, Saudi Arabia to the west, and Yemen to the southwest, and shares marine borders with Iran and Pakistan. The coast is formed by the Arabian Sea on the southeast and the Gulf of Oman on the northeast.
The Omani people are friendly and welcoming and embrace foreign, expat workers with great natural beauty: spectacular mountains, deserts and a pristine coastline. Oman is ideal for those seeking adventure. Historically, Muscat was the principal trading port of the Persian Gulf region. Muscat was also among the most important trading ports of the Indian Ocean. Oman’s official religion is Islam.
Oman is an absolute monarchy. Sultan Qaboos bin Said al Said has been the hereditary leader of the country since 1970. Sultan Qaboos is the longest-serving current ruler in the Middle East, and third-longest current reigning monarch in the world.
Quick Facts:
Capital City: Muscat
Ruler: Sultan Qaboos bin Said al Said
International dialing code: +968
Currency: Omani rial (OMR)
Government: Unitary state, Islamic state, Absolute monarchy
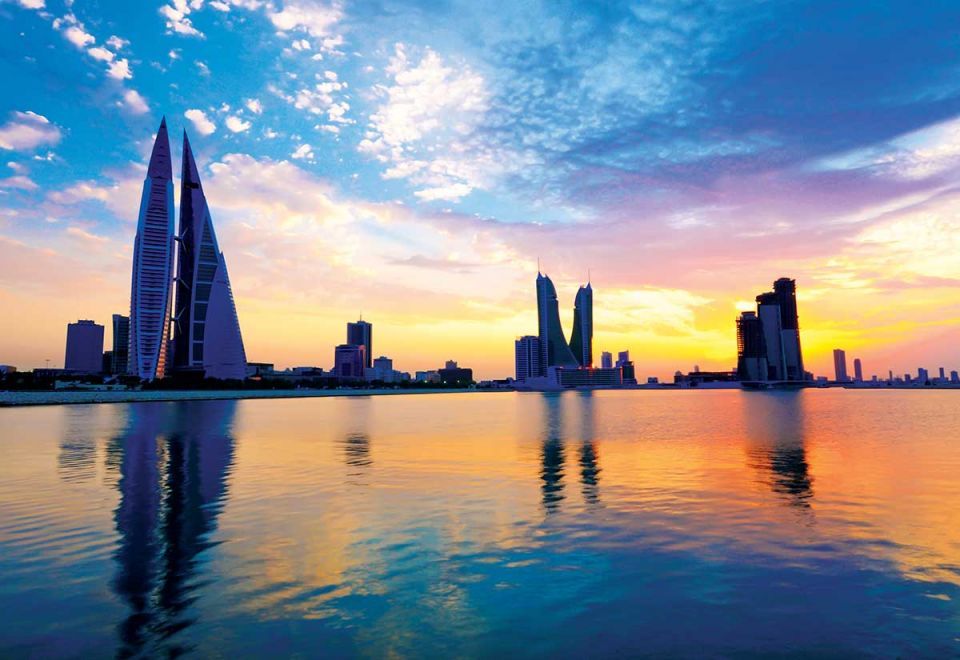
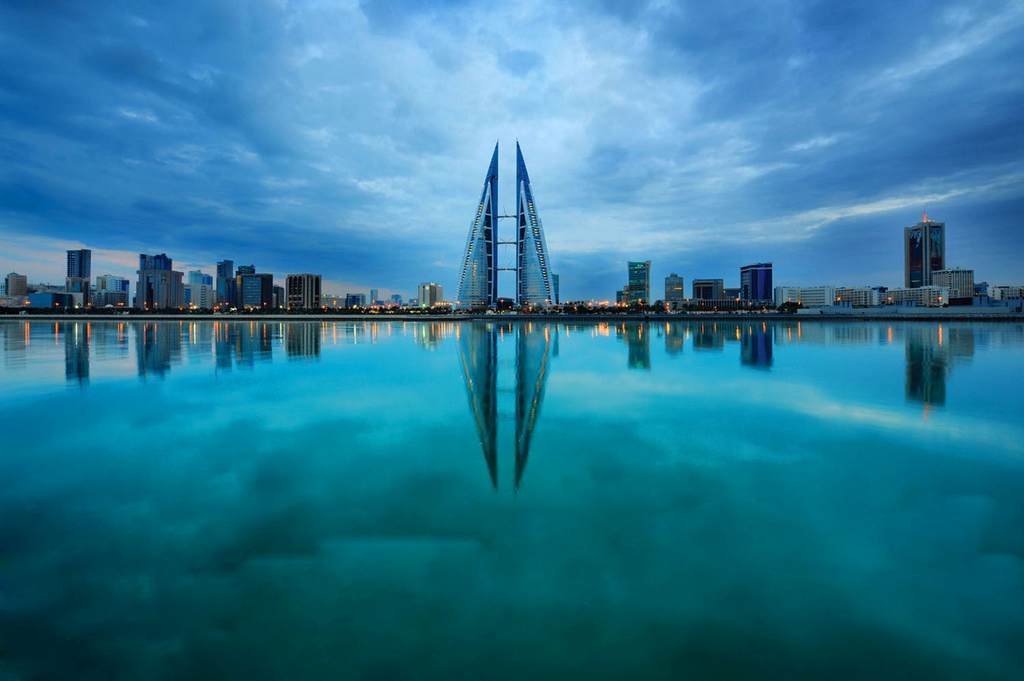
Working and Teaching in Bahrain
Bahrain, officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, is an Arab constitutional monarchy in the Persian Gulf. It is an island country consisting of a small archipelago centered around Bahrain Island, situated between the Qatar peninsula and the north eastern coast of Saudi Arabia.
Bahrain was one of the earliest areas to convert to Islam (AD 28). Following a period of Arab rule and was occupied by the Portuguese in 1521, who in turn were expelled in 1602 by Shah Abbas I of the Safavid dynasty under the Persian Empire. In 1783, the Bani Utbah clan captured Bahrain from Nasr Al-Madhkur and it has since been ruled by the Al Khalifa royal family, with Ahmed al Fateh as Bahrain’s first hakim.
Bahrain had the first post-oil economy in the Persian Gulf and is a great working destination of choice for Western expats. Since the late 20th century, Bahrain has invested heavily in the banking and tourism sectors. Many large financial institutions have a presence in Manama, the country’s capital. Bahrain has a high Human Development Index and was recognised by the World Bank as a high-income economy.
Quick Facts:
Capital City: Manama
Currency: Bahraini dinar (BD)
Population: 1.566 million (2018)
King: Hamad bin Isa Al Khalifah
Government: Monarchy, Constitutional monarchy
Working in Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a sovereign Arab state in Western Asia constituting the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula. With a land area of approximately 2,150,000 km2(830,000 sq mi), Saudi Arabia is geographically the fifth-largest state in Asia and second-largest state in the Arab world after Algeria.
The area of modern-day Saudi Arabia formerly consisted of four distinct regions: Hejaz, Najd and parts of Eastern Arabia (Al-Ahsa) and Southern Arabia (‘Asir). The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia was founded in 1932 by Ibn Saud. He united the four regions into a single state through a series of conquests beginning in 1902 with the capture of Riyadh, the ancestral home of his family, the House of Saud. Saudi Arabia has since been an absolute monarchy, effectively a hereditary dictatorship governed along Islamic lines. The state has a total population of 28.7 million, of which 20 million are Saudi nationals and 8 million are foreigners. The state’s official language is Arabic.
The country is currently undergoing many cultural changes with the introduction of tourist visas later this year and with cinemas having recently been reopened as well as woman gaining the right to drive from July 2018. The dress code in Saudi Arabia is strict with women having to Saudi Arabia has quite a strict dress code with women normally wearing an abaya when in public. Most expatriate teachers and other Western oil/gas/construction professionals live in expatriate gated communities(compounds) with amenities like movie theatres, pools, shops etc. Normal clothing can be worn within these compounds.
Quick Facts:
King: Salman of Saudi Arabia
Capital City: Riyadh
International dialing code: +966
Currency: Saudi riyal (SAR)
Population: 28.29 million (2012)
Working in Qatar
Qatar, officially the State of Qatar is a sovereign country located in Western Asia, occupying the small Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula. Its sole land border is with Saudi Arabia to the south, with the rest of its territory surrounded by the Persian Gulf. An arm of the Persian Gulf separates Qatar from the nearby island country of Bahrain.
Qatar is surrounded by water and offers plenty of different activities from water sports, dune bashing, desert safaris, shopping and attractions including museums, water parks and great restaurants.
Following Ottoman rule, Qatar became a British protectorate in the early 20th century until gaining independence in 1971. Qatar has been ruled by the House of Thani since the early 19th century. Sheikh Jassim bin Mohammed Al Thani was the founder of the State of Qatar. Qatar is a hereditary monarchy and its head of state is Emir Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani. In early 2017, Qatar’s total population was 2.6 million: 313,000 Qatari citizens and 2.3 million expatriates. Islam is the official religion of Qatar.
Qatar is a high-income economy, backed by the world’s third-largest natural-gas reserves and oil reserves. The country has the highest per capita income in the world. Qatar will host the 2022 FIFA World Cup, becoming the first Arab country to do so.
Quick Facts:
Ruler: Emir Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani
Capital City: Doha
International dialing code: +974
Currency: Qatari riyal (QAR)
Population: 2.051 million (2012)
Government: Emirate, Monarchy, Absolute monarchy
Working in Egypt
Egypt, officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia by a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. Egypt is a Mediterranean country bordered by the Gaza Strip and Israel to the northeast, the Gulf of Aqaba to the east, the Red Sea to the east and south, Sudan to the south, and Libya to the west.
Egypt emerged as one of the world’s first nation states in the tenth millennium BC. Considered a cradle of civilisation, Ancient Egypt saw some of the earliest developments of writing, agriculture, urbanisation, organised religion and central government. Iconic monuments such as the Giza Necropolis and its Great Sphinx, as well the ruins of Memphis, Thebes, Karnak, and the Valley of the Kings, reflect this legacy and remain a significant focus of scientific and popular interest.
Egypt’s long and rich cultural heritage is an integral part of its national identity, which has endured, and often assimilated, various foreign influences, including Greek, Persian, Roman, Arab, Ottoman, and Nubian. Egypt was an early and important centre of Christianity, but was largely Islamised in the seventh century and remains a predominantly Muslim country, albeit with a significant Christian minority, the Copts, who reject the Pan-Arab identity that has characterized post-colonial Egypt in the 20th century.
From the 16th to the beginning of the 20th century, Egypt was ruled by foreign imperial powers: The Ottoman Empire and the British Empire. Modern Egypt dates back to 1922, when it gained nominal independence from the British Empire as a monarchy.
Islam is the official religion of Egypt and Arabic is its official language. With over 95 million inhabitants, Egypt is the most populous country in North Africa and the Arab world
Quick Facts:
Capital City: Cairo
President: Abdel Fattah el-Sisi
International Dialing code: +20
Government: Provisional government
Currency: Egyptian pound (EGP)
Official language: Modern Standard Arabic
Working in Jordan
Jordan, officially The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a sovereign Arab state in western Asia, on the East Bank of the Jordan River. Jordan is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the south, Iraq to the north-east, Syria to the north, Israel and Palestine to the west. The Dead Sea lies along its western borders and the country has a small shoreline on the Red Sea in its extreme south-west, but is otherwise landlocked.
What is now Jordan has been inhabited by humans since the Paleolithic period. Three stable kingdoms emerged there at the end of the Bronze Age: Ammon, Moab and Edom. Later rulers include the Nabataean Kingdom, the Roman Empire, and the Ottoman Empire. states to have signed a peace treaty with Israel in 1994. Jordan is a founding member of the Arab League and the Organisation of Islamic Co-operation. The country is a constitutional monarchy, but the king holds wide executiveand legislative powers.
Jordan is a relatively-small, semi-arid, almost-landlocked country with an area of 89,342 km2 (34,495 sq mi) and a population numbering 10 million, making it the 11th-most populous Arab country. Sunni Islam, practiced by around 95% of the population, is the dominant religion in Jordan that coexists with an indigenous Christian minority.
Jordan remains to be considered as among the safest of countries in the Middle East and the country prides itself on being an “oasis of stability” in the region.
Quick Facts:
Ruler: King: Abdullah II of Jordan
Capital: Amman
Currency: Jordanian dinar (JOD)
Population: 9.456 million (2016)
Government: Unitary state, Constitutional monarchy, Parliamentary system
Dialing Code: +962