Qualification Requirements for Working and Teaching in South East Asia and the Far East
K-12 International and IB Curriculum Schools:
- 4 year general BA university degree with PGCE or HDE Diploma
- B.Education Degree in Field of Specialization
- Generally minimum 2 years post-graduate experience preferred but requirements vary
University ESL/ Lecturers
- 4 year general BA university degree with TEFL/TESOL/DELTA
- Masters degrees preferred
- Generally 3 years post-graduate adult teaching experience at university level preferred
Other Professions
- 4 year general BA university degree in field of specialization
- Trade qualifications as per international standards
Salary and Benefits packages)
- Competitive market-related salary commensurate with the industry, qualifications/years of experience
- Flights to some Far Eastern and South Asian countries sometimes have to be paid for by the applicant and the employer will then reimburse the employee in months 3,6, 9 of the first contract.
- Furnished accommodation | accommodation allowance.
- Medical Aid as per the specific countries labour laws.
- Legal work visa valid for 1 or 2 years
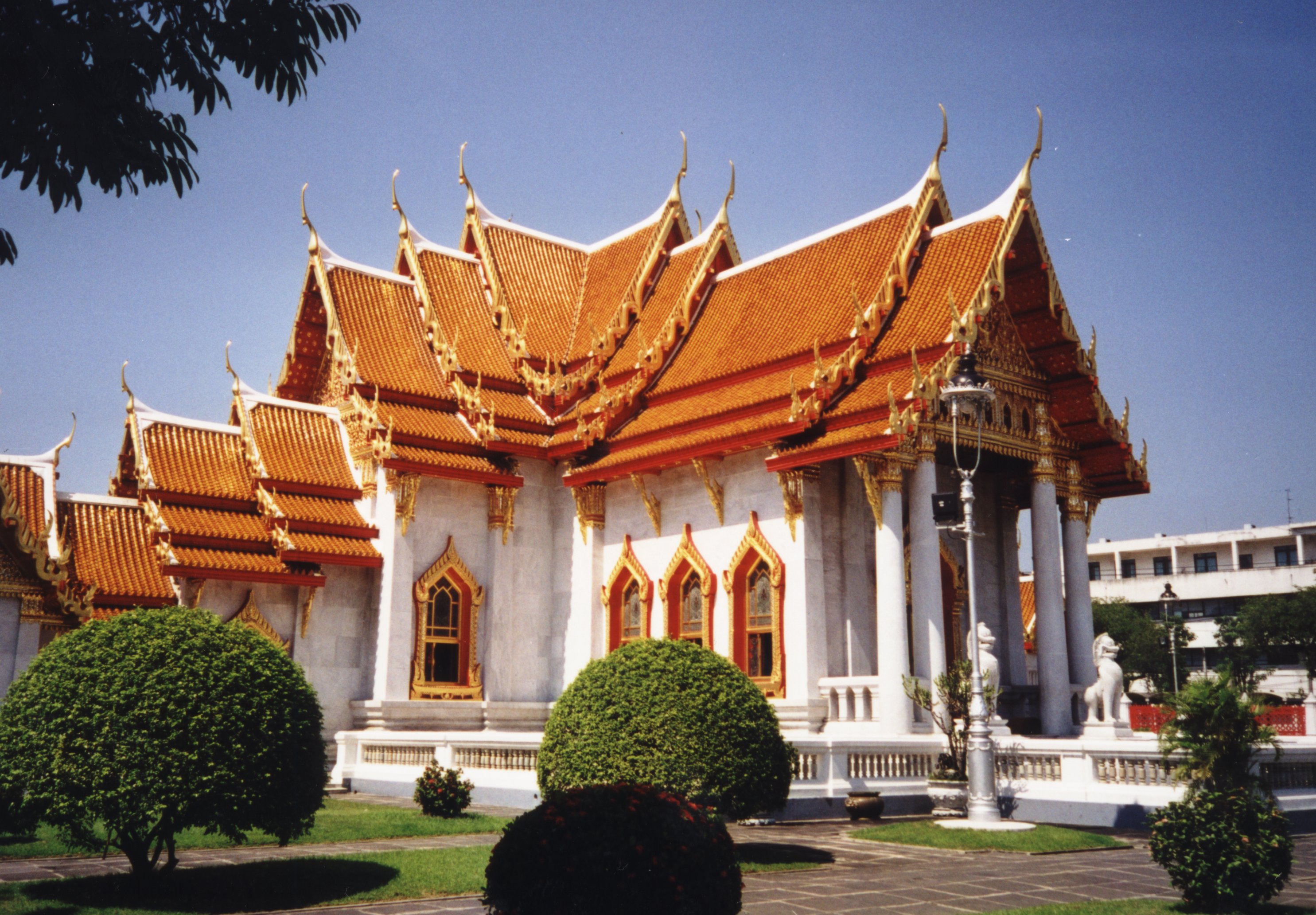
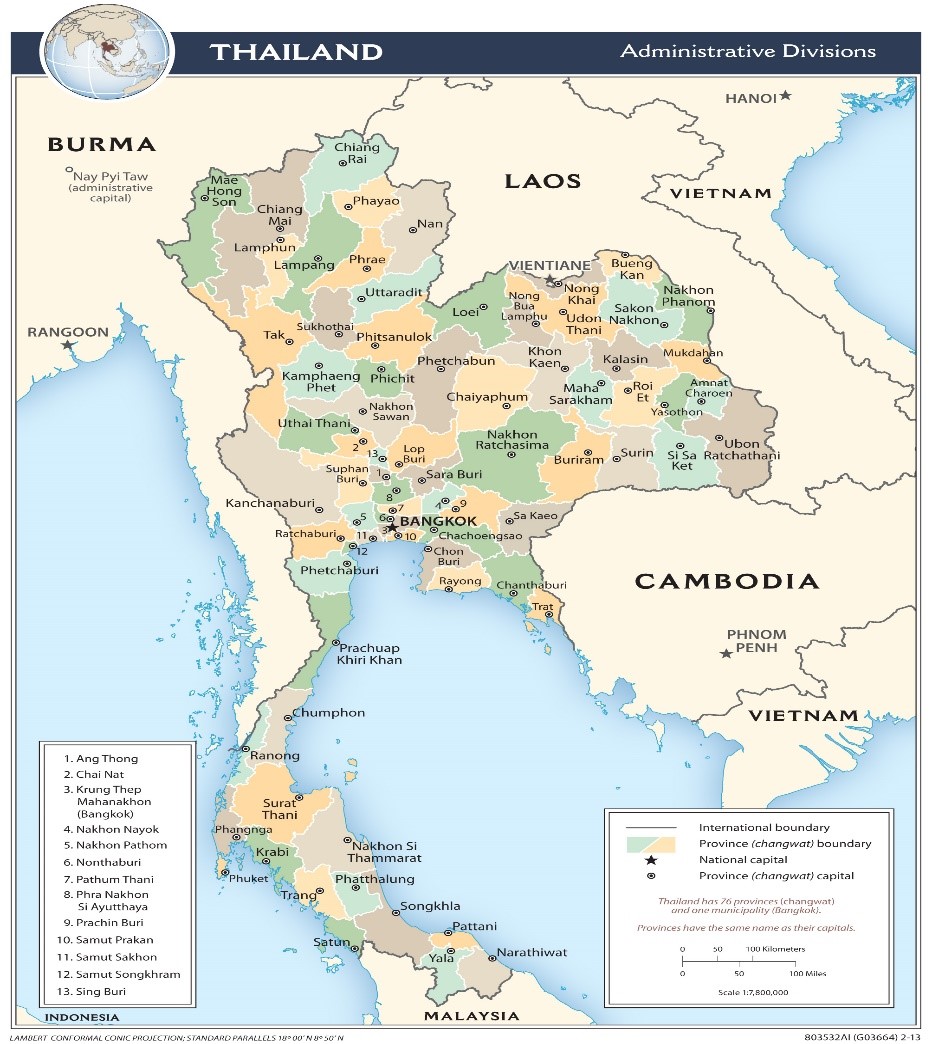
Working and Teaching in Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and formerly known as Siam and the Land of Smiles, is a unitary state at the centre of the Southeast Asian Indochinese peninsula composed of 76 provinces. At 513,120 km2 and over 68 million people, Thailand is the world’s 50th largest country by total area and the 21st-most-populous country
Thailand is a constitutional monarchy. It has a King as a head of state. The current monarch is Vajiralongkorn.
Most of the people of Thailand (95%) follow the philosophy called Buddhism. However, a small number, mostly in the southern part of the country, follow the religion Islam. Other religions in Thailand are Christianity, Hinduism, and Sikhism. Now, some of the Muslims in the south have begun fighting the government of Thailand, because they want to be more independent (free of the control of another country).
The capital and largest city is Bangkok, a special administrative area. Thailand is bordered to the north by Myanmar and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the west by the Andaman Sea and the southern extremity of Myanmar. Its maritime boundaries include Vietnam in the Gulf of Thailand to the southeast, and Indonesia and India on the Andaman Sea to the southwest.
Thailand is classified as a newly industrialized economy; manufacturing, agriculture, and tourism are leading sectors of the economy.
Quick Facts:
Monarch: Maha Vajiralongkorn Bodindradebayavarangkun
Currency: Thai Baht
Capital City: Bangkok
Religions: Buddhism, Islam, Christianity, Hinduism
Language: Thai
Calling Code: +66
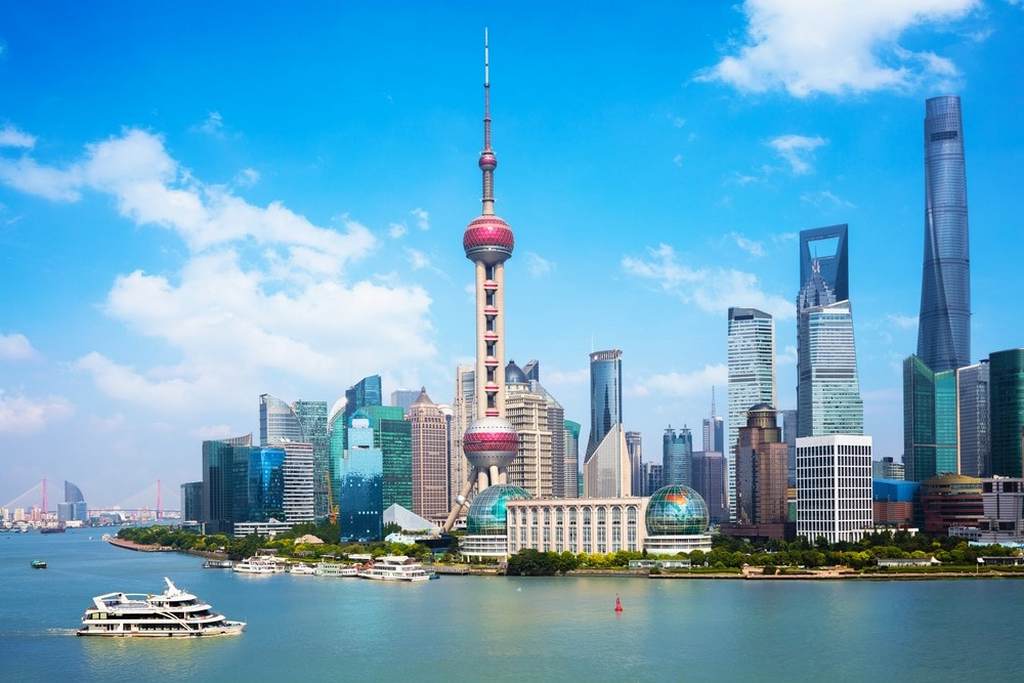
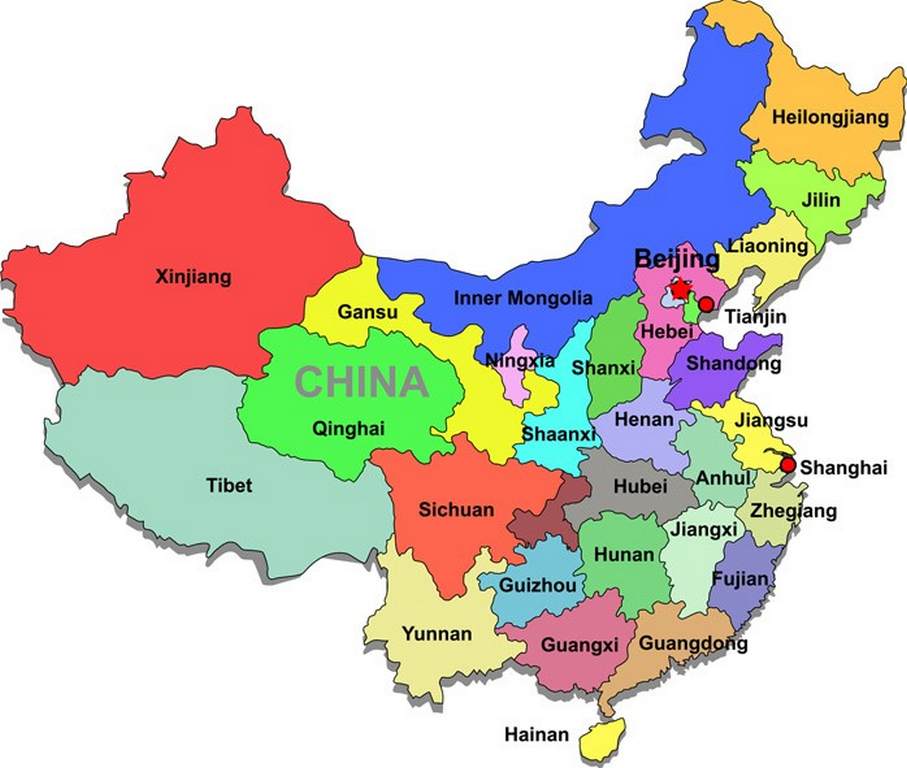
Working and Teaching in China
China, officially the People’s Republic of China (PRC), is a unitary sovereign state in East Asia and the world’s most populous country, with a population of around 1.404 billion. The most populous part is the eastern coastal areas.
China is an ancient country having a profound history. Originated in the eastern area of the Yellow River Region, the country’s civilization is over 5,000 years old and was considered one of four ancient civilizations of the world, along with the civilizations of the ancient Babylon, the ancient Egypt and the ancient India.
The first dynasty of Chinese history started from the Xia Dynasty (2070BC-1600BC) and the last one was the Qing Dynasty (1644-1912), while the most glorious period were the Qin (221BC-206BC), Han (206BC-220), Tang (618-907) and Ming (1368-1644) dynasties. Also, a great amount of cultural relics such as the Great Wall and the Terra Cotta Warriors left by ancestors have become the treasures of the nation and the wonder of the world.
Founded in 1949 by the Communist Party, the People’s Republic of China (PRC) is a unified multi-ethnic country. 56 nationalities are now living in 34 direct administrative regions including 23 provinces, five autonomous regions, four directly-governed city regions–Beijing, Shanghai, Tianjin and Chongqing and two special administrative regions (SAR)–Hong Kong and Macau. The 55 ethnic minorities mainly live in Chongqing, Gansu, Guangxi, Guizhou, Hainan, Heilongjiang, Hubei, Hunan, Inner Mongolia, Jilin, Liaoning, Ningxia, Qinghai, Sichuan, Tibet, Xinjiang and Yunnan.
Quick Facts
President: Xi Jinping
Capital: Beijing
Language: Standard Chinese
Currency: Renminbi (Yuan) CNY
Calling Code: +86



Working and Teaching in Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC) is a region in East Asia. It is the nationalist government of China since its settlement in 1949.
The Chinese Nationalist government (Kuomintang abbreviated as KMT) moved to Taiwan after the Communist army took over the capital of Beijing. Currently, the Chinese Nationalist government governs Taipei, the capital of Taiwan. Taiwan is southeast of the China mainland, south of Japan, and north of the Philippines.
Taiwan has also been called Formosa, a Portuguese name which means “beautiful” in Portuguese. The largest cities in Taiwan are the capital, Taipei, and the port city of Kaohsiung.
Most people living in Taiwan (sometimes called Taiwanese) are Han. Taiwan has three large Han groups. They speak different dialects of Chinese and their ancestors came from different places: the Southern Fujianese (from China’s Fujian Province), the Hakka (from China), and Mainlanders (from Mainland China after 1948).
Quick Facts
President: Tsai Ing -wen
Capital: Taipei
Languages: Standard Chinese, Taiwan Hokkien, Formosan Languages, Hakka
Currency: New Taiwan Dollar (TWD)
Calling Code: + 886
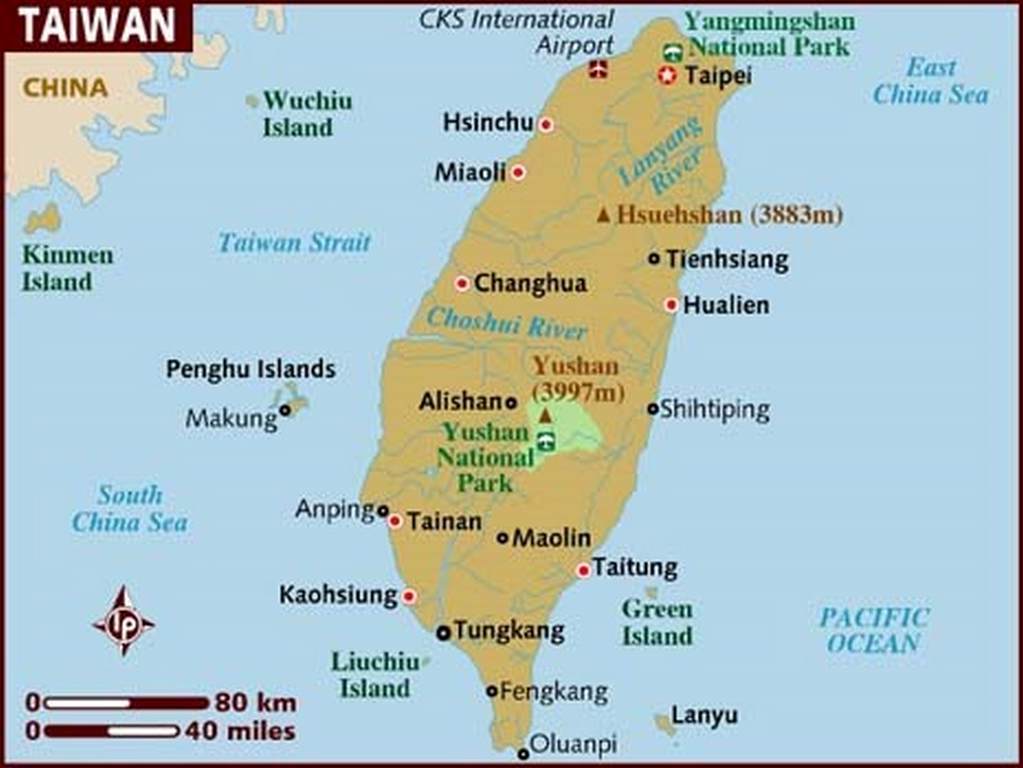


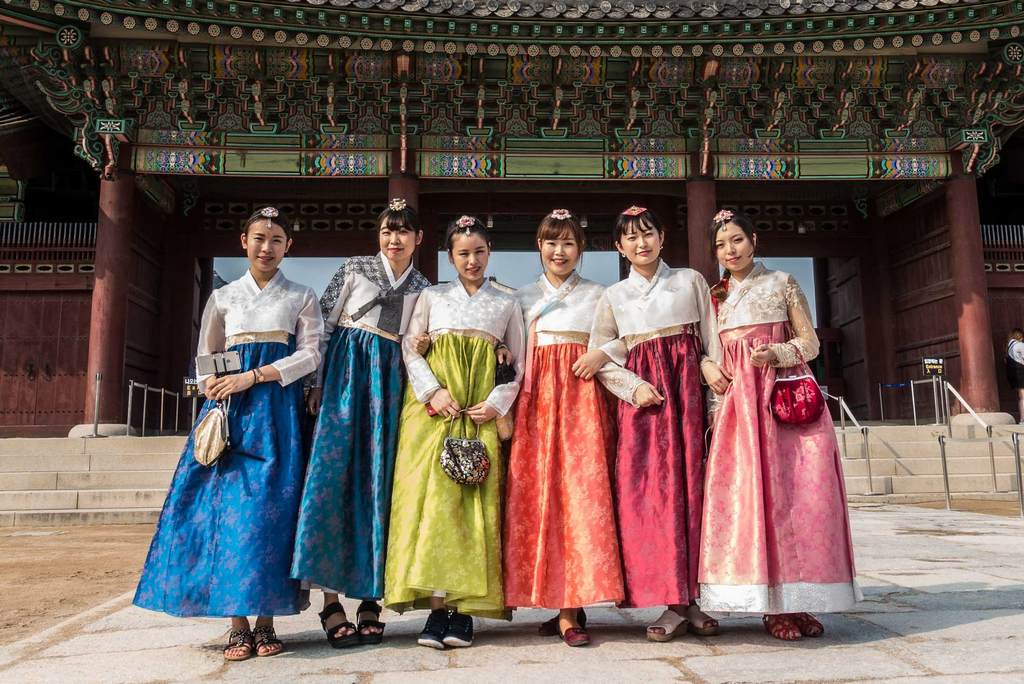
Working and Teaching in South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korean Peninsula. The name Korea is derived from Goryeo, a dynasty which ruled in the Middle Ages. It shares land borders with North Korea to the north, and oversea borders with China to the west and Japan to the east. South Korea lies in the north temperate zone with a predominantly mountainous terrain.
It comprises an estimated 50 million residents distributed over 99,392 km2 (38,375 sq mi). The capital and largest city is Seoul, with a population of 10 million.
The Korean War began in 1950 when forces from the North invaded the South. The war lasted three years and involved the U.S., China, the Soviet Union, and several other nations. In the decades that followed, the South Korean economy grew significantly and the country was transformed into a G-20 major economy.
The border between the two nations remains the most heavily fortified in the world, but an historic meeting took place on 28th April 2018 between General Kim Jung Un and President Moon Jae-in at the DMZ with renewed hopes for peace and the unification of the two Koreas after more than 6 decades.
Quick Facts
President: Moon Jae-in
Capital City: Seoul
Language: Korean
Religion: Protestant, Catholic, Buddhist
Currency: South Korean Won (KRW)
Calling code: + 82
Working and Teaching in Brunei
Brunei, officially the Nation of Brunei, is a sovereign state located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its coastline with the South China Sea, the country is completely surrounded by the Malaysian state of Sarawak. It is separated into two parts by the Sarawak district of Limbang. Brunei is the only sovereign state completely on the island of Borneo; the remainder of the island’s territory is divided between the nations of Malaysia and Indonesia. Brunei’s population was 423,196 in 2016
During the 19th century, the Bruneian Empire began to decline. The Sultanate ceded Sarawak (Kuching) to James Brooke and installed him as the White Rajah, and it ceded Sabah to the British North Borneo Chartered Company. In 1888, Brunei became a British protectorate and was assigned a British resident as colonial manager in 1906. After the Japanese occupation during World War II, in 1959 a new constitution was written. In 1962, a small armed rebellion against the monarchy was ended with the help of the British.
Brunei gained its independence from the United Kingdom on 1 January 1984. Economic growth during the 1990s and 2000s, with the GDP increasing 56% from 1999 to 2008, transformed Brunei into an industrialised country. It has developed wealth from extensive petroleum and natural gas fields. Brunei has the second-highest Human Development Index among the Southeast Asian nations, after Singapore, and is classified as a “developed country.
Quick Facts:
Ruler: Hassanal Bolkiah
Capital City: Bandar Seri Begawan
Language: Malay (Official), English(Recognized)
Religion: Sunni Islam
Currency: Brunei Dollar (BND)
Calling Code: + 673
Working and Teaching in Singapore
The Republic of Singapore is an island country and city-state at the southern end of the Malay Peninsula in Asia. Singapore is north of the equator. Its closest neighbours are Malaysia and Indonesia. About 5.40 million people live in Singapore, of which 3.31 million are citizens, and most of them (76%) are Chinese. In Tamil, an old Indian language, “Singapura”, from which Singapore got its name, means “Lion City” commonly ruled by Sultans.
Singapore is also commonly known as a “Garden City” or a “City in a Garden” because there are plants everywhere, making it look like a garden.
The national language of Singapore is Malay and the other official languages of Singapore are English, Mandarin and Tamil. English is the language of choice because it is the language that almost everyone in Singapore knows. It is the first language taught in schools and the language used by the government. Students are also taught their first language. This means that the Chinese will learn Mandarin and the Malays will learn Malay, and so on. Students can also choose to learn a third language in secondary school.
Quick Facts:
President: Halimah Yacob
Capital City: Singapore
Languages: English, Tamil, Mandarin and Malay
Currency: Singapore Dollar (SGD)
Calling Code: +65
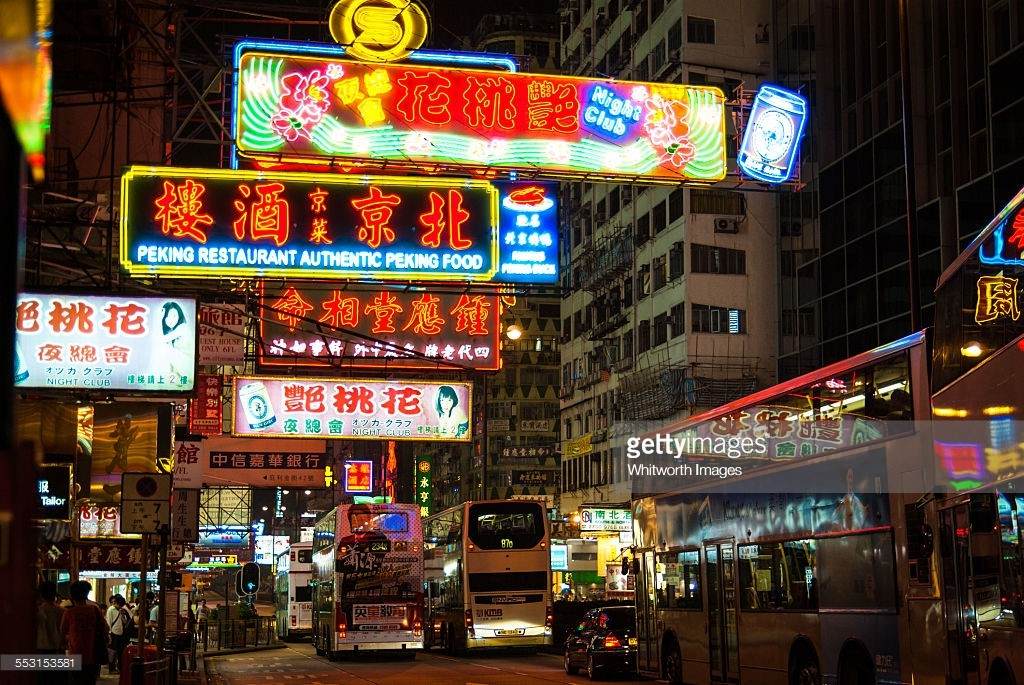
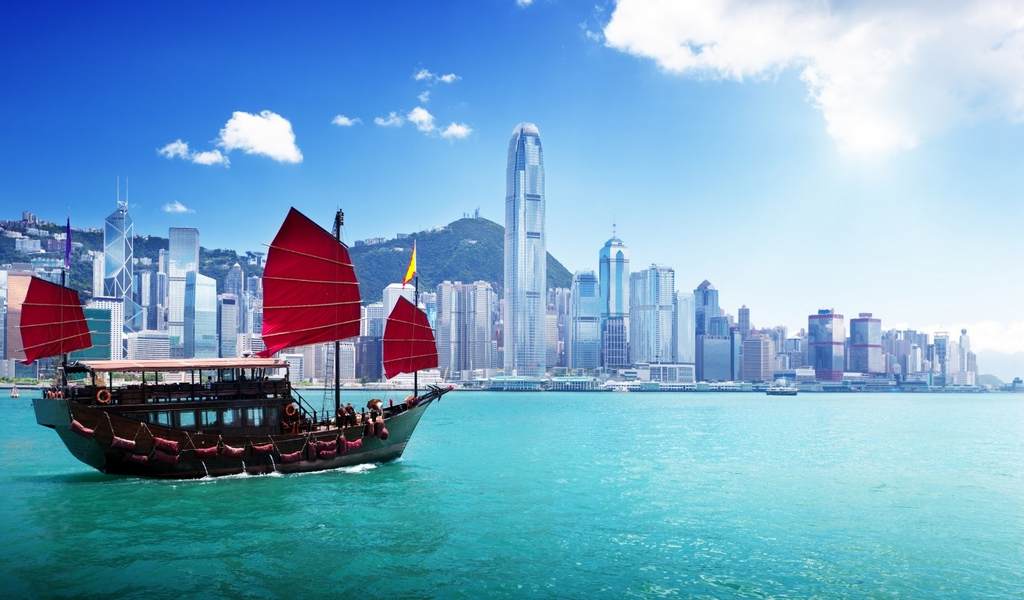
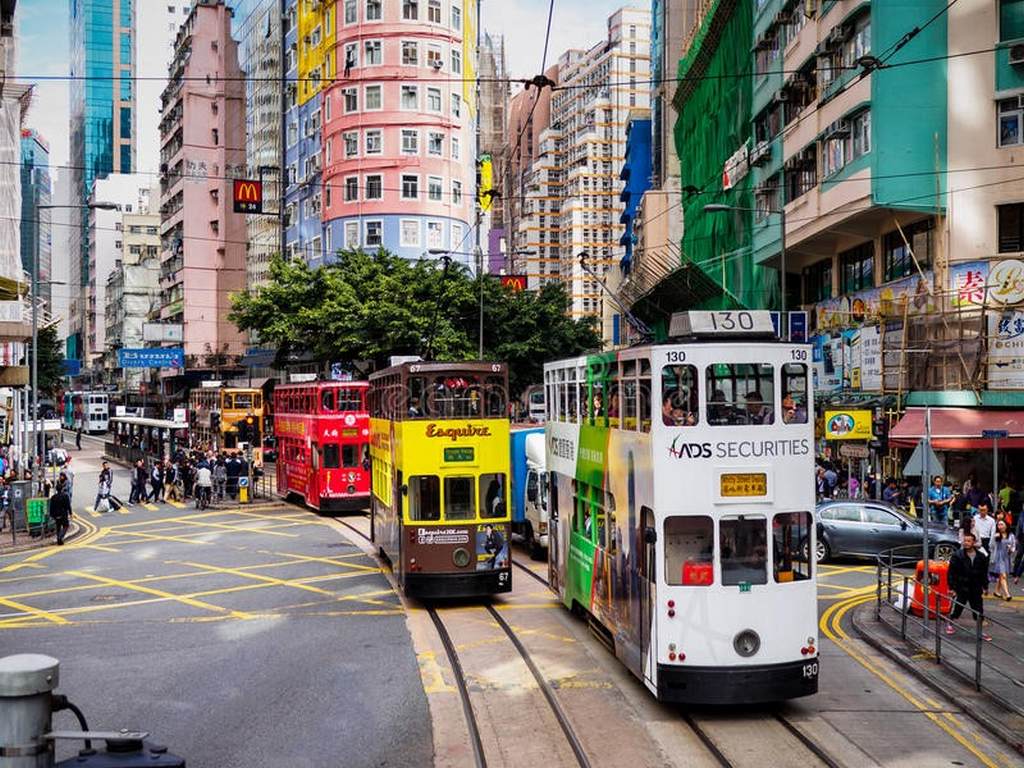
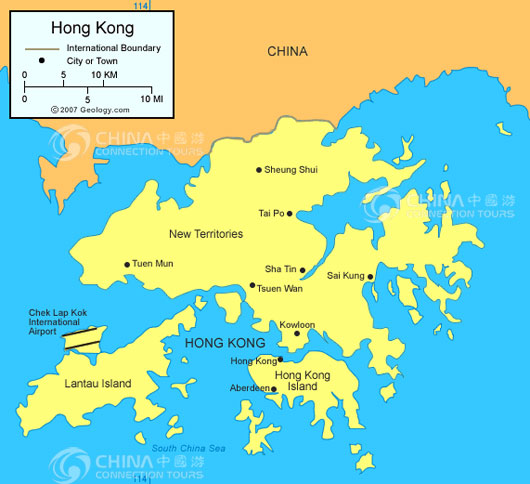
Working and Teaching in Hong Kong
The Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, literally “Fragrant Port” is one of two Special Administrative Regions (SARs) of the People’s Republic of China (the other is Macau). It is one of the richest and most highly developed places in China and even the world. Hong Kong grew quickly in the decades after World War II. It is now a famous world class financial center.
The economy has rapidly grown from a trading port to a very rich city. The population of Hong Kong reached 7 million in 2009. Most of the people in Hong Kong are Chinese. Hong Kong is one of the most densely populated countries in the world. It has an overall density of 6,300 people per square kilometre.
Hong Kong is divided into 3 main parts:
Hong Kong Island
Kowloon
New Territories (including 235 outlying islands)
Hong Kong was a British colony from 1842 to 1997 because China lost the Second Opium War. After the Handover, Hong Kong became a part of China.
People from Hong Kong mainly speak Cantonese. Students are required to learn English at school. Ever since Hong Kong became a part of China, the number of people who speak Mandarin has increased because Mandarin is the official language of the PRC. Some schools have a different track for each of the three languages, depending on the language the student is most comfortable with, and teach all non-language subjects (e.g Maths, science etc.) in the language of the track.
Quick Facts:
Chief Executive: Carrie Lam
Languages: Chinese and English
Currency: Hong Kong Dollar (HKD)
Calling Code: +852